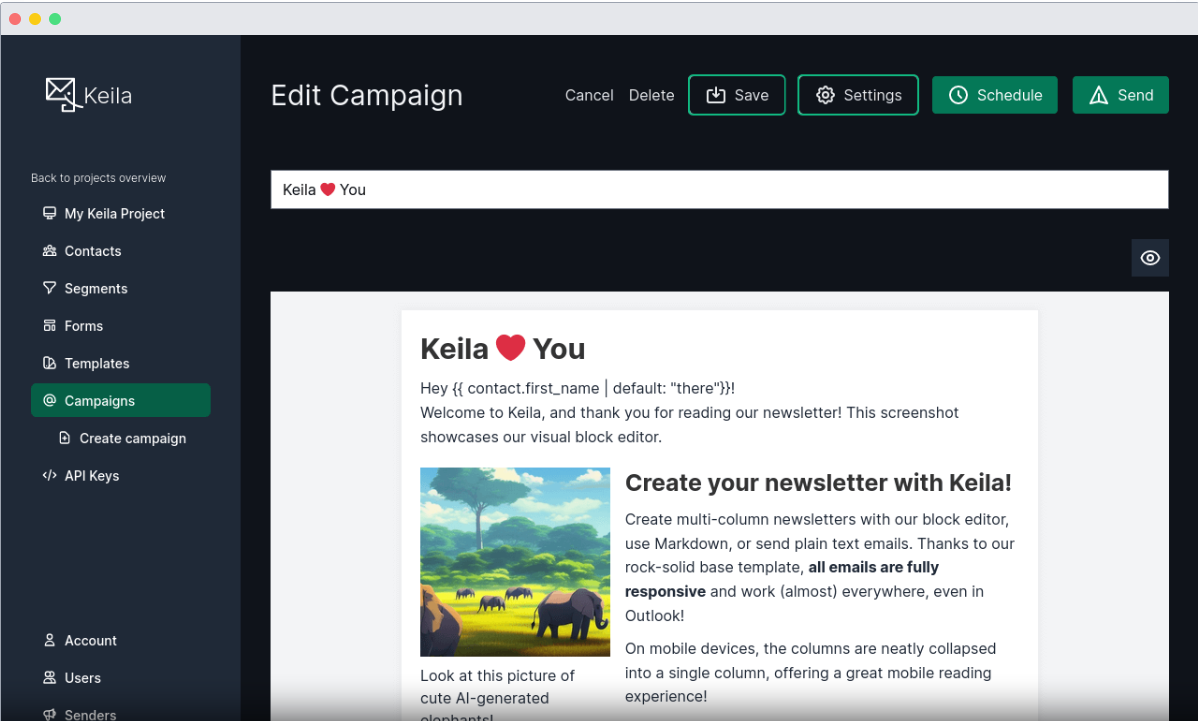
Keila is a powerful, open-source, self-hosted newsletter platform that provides a privacy-focused alternative to mainstream email marketing tools like Mailchimp. It supports list management, email campaigns, automation, and analytics while allowing you to maintain control over your data.
In this guide, we’ll walk through deploying Keila on a server using Docker, setting up SMTP for email delivery, and configuring the platform for production use.
Why Choose Keila? (An Open-Source Alternative to Mailchimp)
Keila is a robust, self-hosted email marketing platform designed for businesses, organizations, and developers who need a privacy-respecting, cost-effective, and customizable solution. Unlike proprietary SaaS solutions like Mailchimp, Keila allows complete ownership of your subscriber data, giving you more control over how emails are sent and tracked. Here’s why Keila is an excellent choice:
1. Self-Hosted for Full Data Control
When using third-party newsletter services like Mailchimp, your email subscriber data is stored on external servers that may be subject to data sharing policies. With Keila, your subscriber list, email campaigns, and analytics are hosted on your own server, ensuring full GDPR compliance and complete data privacy.
2. Cost-Effective Compared to SaaS Platforms
Many email marketing services charge based on the number of subscribers or emails sent per month. Keila is 100% free and open-source, meaning you only pay for your server and SMTP email sending costs. This can significantly reduce email marketing expenses, making it an ideal Mailchimp alternative for startups, nonprofits, and small businesses.
3. No Sending Limits – Scale as Needed
Most email marketing tools impose sending limits based on subscription tiers. With Keila, you can send unlimited emails, provided you configure a reliable SMTP service like Postmark, Mailgun, Amazon SES, or a self-hosted SMTP server.
4. Modern & Intuitive UI
Keila features a modern, user-friendly dashboard similar to Mailchimp, allowing users to easily create, schedule, and send newsletters. It also provides subscriber segmentation, email automation, and detailed campaign analytics for tracking engagement.
5. Built-In Analytics & Open Tracking
Keila includes detailed email tracking and campaign performance analytics, including:
- Open rates
- Click-through rates (CTR)
- Bounce rates
- Unsubscribes
Unlike Mailchimp, which may block tracking unless you upgrade to premium plans, Keila provides real-time insights into your email marketing campaigns without hidden costs.
Prerequisites
Before we start, ensure you have:
A Linux server (Ubuntu 22.04 recommended) or a cloud VPS (DigitalOcean, Linode, AWS, etc.).
Docker & Docker Compose installed.
A domain name with DNS configured for email sending.
An SMTP provider (Postmark, Mailgun, Amazon SES, or self-hosted SMTP like Postfix).
Step 1: Install Docker & Docker Compose
First, update your system and install Docker:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install -y docker.io docker-compose
Enable and start Docker:
sudo systemctl enable --now docker
Verify installation:
docker --version
docker-compose --version
Step 2: Set Up Keila with Docker Compose
Navigate to the /opt directory (or any directory where you prefer to store your Keila installation) and create a folder for Keila:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/keila && cd keila
This will be your working directory where you store all Keila-related files, including the docker-compose.yml and Dockerfile.
Now, create a docker-compose.yml file inside the /opt/keila directory:
nano docker-compose.yml
Then, paste the following content:
version: '3.8'
services:
keila:
image: pentacent/keila:latest
container_name: keila_instance
depends_on:
- db
volumes:
- keila_user_uploads:/app/uploads
build:
context: ../
dockerfile: /opt/keila/Dockerfile
environment:
DB_URL: "postgres://keila_user:keila_password@db:5432/keila_db"
SECRET_KEY_BASE: "your_secret_key"
MAILER_SMTP_FROM_EMAIL: "noreply@example.com"
DISABLE_REGISTRATION: "true"
USER_CONTENT_DIR: "/app/uploads"
OUTBOUND_MAIL_PROVIDER: "smtp"
URL_HOST: "email.example.com"
URL_PORT: "443"
KEILA_USER: "your_keila_user@example.com"
KEILA_PASSWORD: "your_keila_password"
MAILER_SMTP_HOST: "smtp.example.com"
MAILER_SMTP_PORT: "587"
MAILER_SMTP_USERNAME: "your_smtp_user"
MAILER_SMTP_PASSWORD: "your_smtp_password"
CAPTCHA_SITE_KEY: "your_captcha_site_key"
CAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY: "your_captcha_secret_key"
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:4000:4000"
restart: unless-stopped
db:
image: postgres:15
container_name: keila_db_instance
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: keila_user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: keila_password
POSTGRES_DB: keila_db
volumes:
- keila_db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
keila_db_data:
keila_user_uploads:
Explanation of the Docker Compose File
services:Defines a service namedkeila.image: pancodemakes/keila:latestUses the latest pre-built Keila image from Docker Hub.
container_name: keilaAssigns the container a custom name.
restart: alwaysEnsures the container restarts automatically if it crashes.
environment:Sets up environment variables for Keila, including:
BASE_URL: The domain where Keila is hosted (replaceyourdomain.com).SMTP_*: SMTP configuration for sending emails (replace with actual email provider details).
volumes:Mounts a local
datafolder to/app/datain the container for persistent storage.
ports:Maps port
4000on the host machine to port4000inside the container.127.0.0.1:4000:4000ensures it is only accessible locally.
Step 3: Create the Dockerfile
Although we are pulling a pre-built Keila image, if you need to customize it, you can create a Dockerfile inside the keila directory:
nano Dockerfile
Then, paste the following content:
FROM elixir:1.15-alpine as build
ENV MIX_ENV=prod
RUN apk add git npm build-base cmake
COPY mix.exs mix.lock ./
COPY config .
RUN mix local.hex --force && \
mix local.rebar --force && \
mix deps.get && \
mix deps.compile
COPY assets/package.json assets/package-lock.json ./assets/
RUN npm ci --prefix ./assets
COPY . .
RUN mix deps.clean mime --build && \
mix assets.deploy && \
mix release
FROM elixir:1.15-alpine
ENV HOME=/opt/app
WORKDIR ${HOME}
COPY --from=build _build/prod/rel/keila ${HOME}
RUN mkdir -p ${HOME} && \
adduser -s /bin/sh -u 1001 -G root -h ${HOME} -S -D default && \
chown -R 1001:0 ${HOME}
ENTRYPOINT ["/opt/app/bin/keila"]
CMD ["start"]
ARG PORT=4000
ENV PORT=${PORT}
EXPOSE ${PORT}/tcp
Step 4: Run Keila
Once the docker-compose.yml and Dockerfile are ready, start the Keila container:
docker-compose up -d
This will:
Download the Keila image if it’s not already available.
Start the Keila container in detached mode (
-dflag runs it in the background).Bind the configured ports and environment variables.
You can check if the container is running with:
docker ps
Step 5: Secure Keila with a Reverse Proxy
If you want to make Keila accessible over the internet, you should set up a reverse proxy with Nginx and Let’s Encrypt SSL
1. Install Nginx
sudo apt install nginx -y
2. Create an Nginx Configuration File for Keila
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/keila
Add the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:4000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
3. Enable the Configuration and Restart Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/keila /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo systemctl restart nginx
4. Secure with Let’s Encrypt (Free SSL):
Install Certbot and obtain an SSL certificate:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
sudo certbot --nginx -d yourdomain.com
Certbot will automatically configure SSL for your domain.
following this guide, you have successfully deployed Keila on your server using Docker Compose. Keila is a robust, privacy-focused email marketing platform that allows you to send newsletters efficiently while maintaining control over your data.
For more advanced configurations, check out Keila’s official documentation.
Have Any Project Plan In Your Mind?
Get in touch with us for expert consultancy to enhance your digital presence and boost your sales.
-
Mail us 24/7: hello@gcubedinternational.com
-
Call Us: +1 619-535-1715
